Contact Lens Safety: How Common Eye Care Mistakes Can Lead to Vision Loss
The Hidden Dangers of Overnight Contact Lens Wear
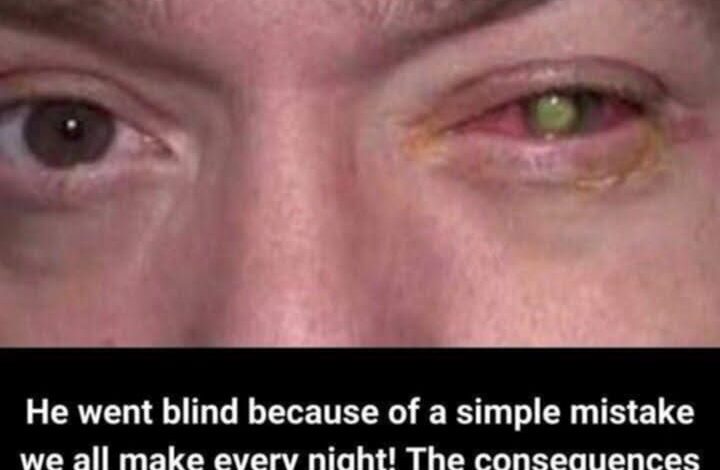
A 39-year-old business owner named Groeschen recently experienced a life-changing eye health crisis that serves as a critical warning for millions of contact lens users. His experience highlights the serious risks associated with improper contact lens hygiene and overnight wear practices.
Understanding the Medical Emergency
Groeschen initially noticed mild eye irritation upon waking, which progressively worsened over several days. Seeking professional medical attention at the Cincinnati Eye Institute, ophthalmologists diagnosed him with a severe Pseudomonas bacterial infection directly linked to his habit of sleeping while wearing contact lenses.
The bacterial infection proved particularly aggressive, thriving in the moist environment created beneath his contact lenses during overnight wear. This bacterial growth caused significant corneal erosion, resulting in substantial vision impairment and long-term eye health complications.
The Extent of Vision Damage
Medical professionals described Groeschen’s vision loss as comparable to “viewing through frosted glass,” illustrating the severity of corneal damage caused by the bacterial infection. Even after successful treatment of the active infection, permanent scar tissue formation on the cornea continued to impair his vision.
The only viable treatment option for restoring his sight involves corneal transplant surgery, a major ophthalmological procedure requiring extensive recovery time of approximately one year. This surgical intervention represents the most advanced treatment available for severe corneal scarring.
Impact on Professional and Personal Life
As the owner of a design restoration company, Groeschen faced significant professional challenges due to his vision impairment. The eye health crisis forced him to temporarily cease business operations, demonstrating how contact lens-related complications can affect livelihood and financial stability.
Contact Lens Marketing vs. Medical Recommendations
Groeschen noted that his contact lens packaging included marketing claims suggesting overnight wear was safe for extended periods. However, these manufacturer claims contradict established medical guidelines and professional ophthalmological recommendations.
The American Academy of Ophthalmology issued clear warnings in 2013 regarding the substantial increased risk of eye infections associated with sleeping in any type of contact lenses, regardless of manufacturer claims about extended wear safety.
Professional Medical Advice on Contact Lens Hygiene
Dr. William Faulkner, Groeschen’s treating physician, emphasizes several critical contact lens safety protocols:
Never Sleep in Contact Lenses: Regardless of manufacturer claims, overnight wear significantly increases bacterial infection risk.
Maintain Proper Lens Case Hygiene: Replace contact lens cases regularly to prevent bacterial accumulation.
Use Fresh Cleaning Solutions: Always use new cleaning solution rather than reusing or topping off existing solution.
Follow Replacement Schedules: Adhere to recommended lens replacement timelines to maintain optimal eye health.
Preventing Contact Lens-Related Eye Infections
This case demonstrates the importance of following proper contact lens care protocols. Eye care professionals recommend:
- Removing lenses before sleep, regardless of type
- Washing hands thoroughly before handling lenses
- Using only sterile saline solutions for cleaning
- Scheduling regular eye examinations with qualified optometrists
- Replacing contact lenses according to prescribed schedules
The Importance of Professional Eye Care
Regular consultation with eye care professionals remains essential for maintaining optimal vision health. Professional eye examinations can detect early signs of complications and provide personalized guidance for safe contact lens use.
Conclusion: Prioritizing Eye Health and Safety
Groeschen’s experience serves as a powerful reminder that proper contact lens hygiene is not optional—it’s essential for preventing serious eye health complications. The convenience of extended wear should never compromise long-term vision health and quality of life.