Essential HPV Health Guide: Symptoms, Prevention, and Treatment Options
Understanding Human Papillomavirus and Its Health Impact
Human papillomavirus represents the most common sexually transmitted infection globally, affecting approximately 80% of sexually active individuals according to CDC health statistics. This widespread virus family encompasses over 150 different strains, making HPV awareness crucial for maintaining optimal sexual health and preventing serious complications.
The challenging aspect of HPV involves its often asymptomatic nature during early stages. Many people carry and transmit the virus without experiencing visible symptoms, creating significant public health concerns. Understanding HPV symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies becomes essential for protecting long-term wellness.
HPV Types and Health Risks
Medical professionals classify HPV into two primary categories based on cancer risk potential. Low-risk HPV strains typically cause benign conditions like genital warts but rarely progress to cancer. High-risk HPV types, particularly strains 16 and 18, pose serious health threats by potentially developing into cervical cancer, throat cancer, and other malignancies if left untreated.
Transmission occurs through skin-to-skin contact during intimate activities, including vaginal, oral, and anal contact. Unlike many other sexually transmitted infections, HPV transmission doesn’t require penetrative intercourse, making prevention strategies particularly important for sexually active individuals.
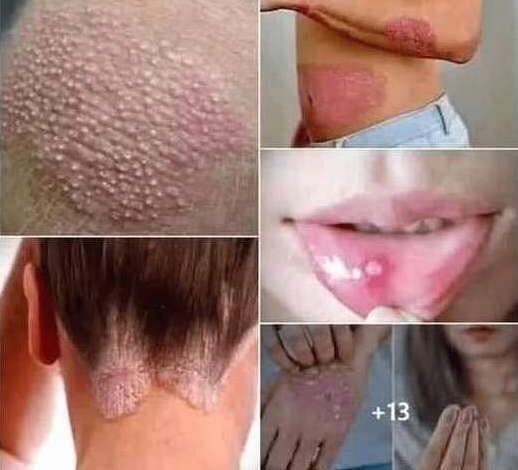
Recognizing HPV Symptoms and Warning Signs
While many HPV infections remain invisible, certain symptoms warrant immediate medical attention. Genital warts represent the most common visible symptom, appearing as small, flesh-colored bumps that may develop cauliflower-like textures. These growths can appear on various genital areas in both men and women.
Women should pay particular attention to abnormal Pap smear results, which often indicate HPV-related cellular changes before visible symptoms develop. Regular gynecological screenings help detect high-risk HPV strains that could progress to cervical cancer without proper medical intervention.
Cancer-related symptoms may include unusual bleeding, persistent pelvic pain, unexplained throat discomfort, or voice changes. These warning signs require prompt medical evaluation to determine appropriate treatment options.
Gender-Specific HPV Considerations
HPV affects men and women differently in terms of health risks and symptom presentation. Women face higher cervical cancer risks, making regular Pap tests and HPV screenings essential preventive measures. Men often carry HPV asymptomatically but remain at risk for genital warts and certain cancers affecting the penis, throat, and anal regions.
Both genders can transmit HPV to sexual partners regardless of symptom presence, emphasizing the importance of open communication about sexual health and regular STI testing.
HPV Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Several lifestyle factors increase HPV transmission risks, including multiple sexual partners, early sexual activity onset, unprotected sexual contact, compromised immune systems, and tobacco use. Understanding these risk factors helps individuals make informed decisions about sexual health practices.
The HPV vaccine provides highly effective protection against the most dangerous viral strains. Healthcare professionals recommend vaccination for both males and females before sexual activity begins, though older individuals may still benefit from vaccination after consulting their physicians.
Treatment Options and Medical Management
While no cure exists for HPV itself, various treatments effectively manage symptoms and prevent complications. Genital warts respond well to topical medications, cryotherapy, laser treatments, or minor surgical procedures. Abnormal cervical cells detected through screening can be treated using LEEP procedures or cryotherapy to prevent cancer development.
HPV-related cancers require comprehensive treatment approaches including surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy depending on cancer stage and location.
Emotional Wellness and HPV Diagnosis
HPV diagnosis can trigger anxiety, shame, or relationship concerns. Mental health support becomes crucial for processing these emotions healthily. Remember that HPV represents an extremely common condition that doesn’t reflect personal character or worth. Healthcare providers, counselors, and support groups offer valuable resources for managing the emotional aspects of HPV diagnosis.
Maintaining Sexual Health and Wellness
Proactive sexual health management includes regular medical screenings, honest communication with partners, consistent safer sex practices, and maintaining strong immune systems through healthy lifestyle choices. These strategies significantly reduce HPV transmission risks while supporting overall wellness goals.