Exercise-Induced Vasculitis: Medical Guide to Heat-Related Skin Conditions
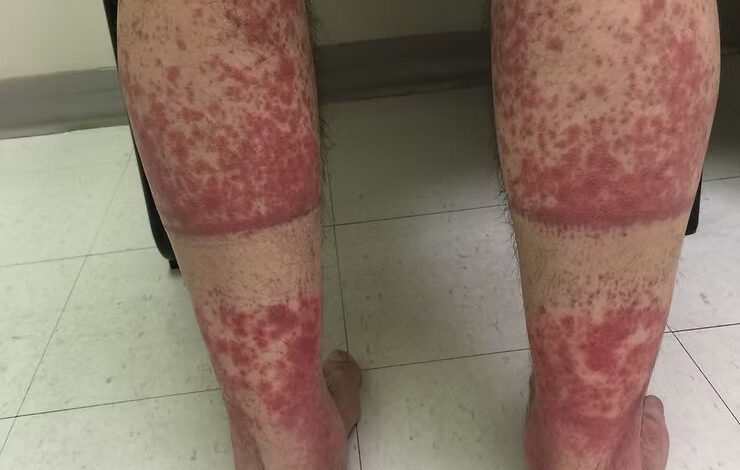
Healthcare professionals frequently encounter patients experiencing unusual skin reactions following outdoor activities and exercise routines in warm weather conditions. One commonly misdiagnosed condition is exercise-induced vasculitis, a vascular disorder that requires proper medical evaluation and dermatological assessment for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
This comprehensive medical guide provides essential information about exercise-induced vasculitis symptoms, diagnostic criteria, and evidence-based treatment approaches recommended by healthcare providers specializing in sports medicine and dermatology.
Understanding Exercise-Induced Vasculitis: Medical Definition and Pathophysiology
Clinical Overview and Vascular Pathology
Exercise-induced vasculitis (EIV) represents a specific type of cutaneous vasculitis triggered by prolonged physical activity in elevated temperatures. Healthcare providers classify this condition as a heat-related inflammatory response affecting small blood vessels, particularly capillaries located in the lower extremities.
Medical research indicates that during extended exercise periods, increased blood circulation combined with heat exposure can lead to blood pooling in dependent limbs. This vascular congestion triggers inflammatory responses in small blood vessels near the skin surface, resulting in characteristic dermatological manifestations requiring medical assessment.
Patient Demographics and Risk Factors
Clinical studies demonstrate that exercise-induced vasculitis predominantly affects specific patient populations with identifiable risk factors:
Primary Risk Categories:
- Adults over 50 years experiencing age-related vascular changes
- Active women participating in regular fitness programs and outdoor activities
- Travel medicine patients engaging in extended walking during vacation activities
- Individuals with circulatory conditions affecting peripheral blood flow
Healthcare providers note increased incidence among cruise ship passengers and vacation travelers who experience prolonged walking in hot climates, highlighting the importance of travel medicine awareness and preventive healthcare education.
Clinical Presentation and Diagnostic Symptoms
Medical Symptom Recognition and Assessment
Healthcare professionals identify exercise-induced vasculitis through specific clinical presentations that distinguish it from other dermatological conditions requiring medical treatment:
Primary Clinical Symptoms:
- Erythematous or purpuric rashes localized to lower extremities
- Distinctive distribution patterns around ankles and lower legs
- Pruritic sensations and burning discomfort requiring symptom management
- Mild edema and localized inflammation in affected areas
Timeline of Symptom Development:
Medical observations indicate that symptoms typically manifest 2-6 hours following prolonged physical activity in heat, with peak intensity occurring within 24-48 hours of initial exposure.
Differential Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Healthcare providers must differentiate exercise-induced vasculitis from other serious medical conditions requiring immediate medical intervention and specialized treatment:
Critical Differential Diagnoses:
Cellulitis and Bacterial Infections:
- Requires immediate antibiotic therapy and medical monitoring
- Presents with fever, localized warmth, and systemic symptoms
- Often affects single extremity with progressive symptoms
Infectious Disease Considerations:
- Folliculitis from contaminated recreational water exposure
- Requires antimicrobial treatment and dermatological care
- Associated with specific exposure history and bacterial cultures
Emergency Medical Conditions:
- Meningococcal rash requiring immediate emergency medical treatment
- Sepsis-related cutaneous manifestations needing critical care intervention
- Non-blanching rashes indicating serious systemic illness
Evidence-Based Treatment Protocols and Medical Management
Conservative Treatment Approaches
Healthcare providers recommend first-line conservative treatment methods for confirmed exercise-induced vasculitis cases:
Primary Medical Interventions:
- Therapeutic cooling therapy using cold compresses for symptom relief
- Postural drainage techniques with leg elevation above cardiac level
- Hydration therapy supporting vascular function and circulation
- Anti-inflammatory medications including over-the-counter antihistamines
Advanced Treatment Options and Medical Monitoring
For patients experiencing recurrent episodes or severe symptoms, healthcare providers may recommend:
Specialized Medical Treatments:
- Compression therapy using medical-grade compression stockings
- Topical corticosteroids for localized inflammatory management
- Systemic medications for patients with severe or persistent symptoms
- Dermatological consultation for complex cases requiring specialist care
Preventive Medicine and Risk Reduction Strategies
Clinical Prevention Protocols
Healthcare professionals emphasize preventive medicine approaches for high-risk patients and individuals with history of exercise-induced vasculitis:
Primary Prevention Measures:
- Exercise physiology optimization through activity modification in hot weather
- Hydration protocols before, during, and after physical activity
- Environmental modification including shade utilization and cooling breaks
- Protective equipment such as breathable athletic wear and sun protection
Travel Medicine and Vacation Health Planning
For patients planning travel or extended outdoor activities, healthcare providers recommend:
Travel Health Consultations:
- Pre-travel medical assessment for vascular risk factors
- Activity planning and environmental exposure management
- Emergency medical care access and treatment protocols
- Travel insurance considerations for medical treatment coverage
When to Seek Professional Medical Care
Emergency Medical Situations
Healthcare providers stress that certain symptoms require immediate medical evaluation and emergency treatment:
Medical Emergency Indicators:
- Rapid symptom progression with systemic illness
- High fever accompanying skin manifestations
- Non-blanching rash patterns suggesting serious conditions
- Severe pain, extensive swelling, or circulatory compromise
Routine Medical Consultation Criteria
Patients should schedule healthcare appointments for professional medical evaluation when experiencing:
Professional Assessment Needed:
- First episode of exercise-related skin reactions
- Recurrent symptoms requiring ongoing medical management
- Uncertainty about diagnosis or treatment effectiveness
- Need for specialist referral to dermatology or vascular medicine
Medical Research and Clinical Studies
Current Healthcare Literature
Recent medical research published in sports medicine and dermatology journals has expanded understanding of exercise-induced vasculitis pathophysiology and treatment protocols. Healthcare professionals utilize evidence-based guidelines from peer-reviewed medical literature to optimize patient care and treatment outcomes.
Research Findings Include:
- Improved diagnostic criteria for clinical identification
- Advanced treatment protocols reducing symptom duration
- Prevention strategies for high-risk patient populations
- Long-term prognosis and recurrence pattern analysis
Future Healthcare Developments
Ongoing medical research focuses on developing improved treatment modalities and prevention strategies for exercise-induced vasculitis. Healthcare innovation in sports medicine and dermatology continues advancing patient care through specialized treatment protocols and diagnostic technologies.
Patient Education and Health Advocacy
Healthcare Provider Communication
Medical professionals emphasize the importance of patient education about exercise-induced vasculitis recognition and appropriate medical response. Clear communication between healthcare providers and patients ensures proper symptom management and prevents unnecessary anxiety about benign conditions.
Patient Education Topics:
- Symptom recognition and home monitoring techniques
- When to seek immediate medical care versus routine consultation
- Prevention strategies for active lifestyle maintenance
- Long-term health management and activity modification
Community Health Awareness
Healthcare organizations promote community education about heat-related medical conditions and exercise safety. Public health initiatives focus on increasing awareness among active adults, travelers, and fitness enthusiasts about proper recognition and management of exercise-induced vasculitis.
Prognosis and Long-Term Medical Management
Clinical Outcomes and Recovery
Healthcare providers report excellent prognosis for patients with exercise-induced vasculitis when properly diagnosed and managed. Most patients experience complete symptom resolution within 7-10 days using conservative treatment approaches under medical guidance.
Positive Prognostic Factors:
- Early recognition and appropriate medical management
- Proper activity modification and environmental controls
- Good baseline health and vascular function
- Compliance with healthcare provider recommendations
Ongoing Healthcare Management
For patients with recurrent episodes, healthcare providers develop individualized management plans including:
Long-term Care Strategies:
- Regular medical monitoring and symptom tracking
- Preventive medicine protocols for high-risk activities
- Lifestyle modifications supporting vascular health
- Specialist consultation when indicated for complex cases
Conclusion: Comprehensive Medical Care and Patient Safety
Exercise-induced vasculitis represents a manageable medical condition when properly diagnosed and treated by healthcare professionals. While generally benign, accurate medical assessment ensures appropriate treatment and prevents misdiagnosis of more serious conditions requiring immediate medical intervention.
Healthcare providers emphasize that patients experiencing unusual skin reactions following exercise should seek professional medical evaluation for proper diagnosis and treatment planning. Early medical consultation, combined with evidence-based treatment approaches, ensures optimal patient outcomes and supports continued participation in healthy lifestyle activities.
Through comprehensive medical care, patient education, and preventive medicine strategies, individuals can safely maintain active lifestyles while minimizing risks of exercise-induced vasculitis and other heat-related medical conditions. Regular healthcare consultation and proper symptom recognition remain essential components of effective long-term medical management and patient safety.